Diabetes Tests in Singapore
Diabetes tests in Singapore typically include the fasting blood glucose (FBG) test, glycated
haemoglobin (HbA1c) test, and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). These screening methods
measure blood sugar levels to diagnose the condition, monitor ongoing treatment, or assess the risk of
developing the condition.
Since diabetes often progresses silently without noticeable early symptoms, regular testing is essential
for early detection and for reducing the likelihood of long-term complications.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a long-term condition where blood sugar levels are consistently higher than normal. This happens when the pancreas produces too little insulin, a hormone that helps glucose move into the body’s cells for energy, or when the body cannot use insulin effectively. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, which over time can damage the heart, kidneys, nerves, eyes, and blood vessels if left unmanaged.

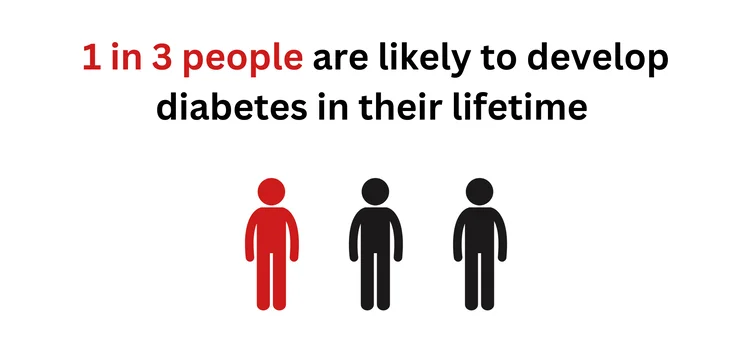
Diabetes Statistics in Singapore
According to the Ministry of Health, more than 400,000 people in Singapore are currently
living with diabetes. This number is expected to grow to 600,000 by 2030 and may
reach 1 million by 2050. Around 1 in 3 people will develop diabetes in their
lifetime.
Because symptoms may be absent or mild in the early stages, routine testing is essential to
detect the disease early and prevent complications.
Types of Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes, along with other related conditions:
- Type 1 diabetes – An autoimmune condition, often inherited, where the immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes – The most common form, often associated with factors such as excess body weight, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and older age.
- Prediabetes – A state where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a Type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
- Gestational diabetes – A type that develops during pregnancy, which can increase the risk of both mother and child developing Type 2 diabetes in the future.
Can Diabetes Be Cured?
There is no definitive cure for diabetes, but some types can enter remission or resolve under
certain conditions.
Type 1 diabetes cannot be cured and requires lifelong treatment to replace insulin. Type 2 diabetes may
enter remission through sustained lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, weight management, and
regular physical activity. If lifestyle changes are insufficient, treatment is needed to control blood
sugar levels. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, but it increases the long-term
risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Regardless of the type, regular monitoring and effective management are essential to maintain healthy
blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
What Are Common Symptoms of Diabetes?
Symptoms of diabetes are typically caused by persistently high blood sugar levels that interfere with normal body functions. Common signs include:
- Persistent thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Constant tiredness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing cuts or wounds
- Repeated infections
Type 2 diabetes can progress with few or no symptoms initially. Without treatment, the condition can lead to serious issues such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, vision impairment, and severe foot problems that may require amputation in extreme cases.

How to Test For Diabetes?
Diagnosis of diabetes is typically carried out through blood glucose testing. Common tests include:
| Test | Description | Blood Glucose Range |
|---|---|---|
| Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Test | Measures blood sugar after an overnight fast. Commonly used to identify early diabetes. |
Normal: <6.1mmol/L (<99 mg/dL) Pre-diabetes: 6.1 - 6.9mmol/L (100 - 125 mg/dL) Type 2 Diabetes: >6.9mmol/L (>125 mg/dL) on two separate tests |
| Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Test | Measures the average blood sugar over the past 2–3 months. No fasting is required. Useful for diagnosis and ongoing monitoring. |
Normal: <6.1% Pre-diabetes: 6.1% - 6.9% (confirmatory OGTT advised) Type 2 Diabetes: >6.9% |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) | Measures blood sugar before and two hours after drinking a glucose solution following an overnight fast. Used for detecting gestational diabetes and confirming pre-diabetes. |
Normal 2h glucose: <7.8mmol/L (<140 mg/dL) Pre-diabetes 2h glucose: 7.8 - 11.0mmol/L (140 - 199 mg/dL) Type 2 Diabetes 2h glucose: >11.0mmol/L (>199 mg/dL) |
A fasting insulin test may also be used to assess insulin resistance or production, especially in cases
involving metabolic disorders.
Adults aged 40 and above are advised to undergo diabetes screening at least once every three years. For those with higher risk
factors, such as obesity, a family history of diabetes, a history of gestational diabetes, or a
diagnosis of prediabetes, screening should be done more often. If you are unsure about how often you
should be screened, consult your doctor for personalised advice.
How Is Diabetes Managed / Treated?
Treatment and management of diabetes focuses on maintaining healthy blood sugar levels to control symptoms and prevent long-term complications. This can include:
- Lifestyle changes – Following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Medications – If lifestyle changes are insufficient, doctors may prescribe oral medicines to improve insulin function or help the body regulate glucose more effectively.
- Insulin therapy – For individuals who cannot produce enough insulin naturally, injections are necessary to replace the missing hormone and directly regulate blood sugar levels.
- Ongoing monitoring – Routine medical check-ups, home blood sugar testing, and periodic HbA1c tests help track progress and adjust treatment plans.

How Much Do Diabetes Tests Cost in Singapore?
At healthscreening.sg, we offer diabetes testing and continuous glucose monitoring kits for home use. Prices are as follows:
| Test / Treatment | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Test | $10.90 |
| Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Test | $27.25 |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) | $27.25 |
| Fasting Insulin Test | $66.49 |
| Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): FreeStyle Libre | $27.25 (first sensor for first-time users) |
| [Optional] Mobile Blood Drawing Service | $54.50 (per location up to 5 pax) |
| Screen for Life Diabetes Screening | $0 to $5 (depending on CHAS/MG/PG status) |
*Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST.
Eligible Singaporeans and Permanent Residents aged 40 and above may receive subsidies for diabetes
testing under the Health Promotion Board’s Screen for Life (SFL) programme. Contact us to confirm your
eligibility for subsidies.
For a more thorough health review, you may consider our health screening
packages, which include diabetes profile testing.
How to Prepare for Diabetes Testing?
Preparing for diabetes testing depending on the type of test.
- Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Test – Avoid eating or drinking anything except water for at least 8 hours before the test.
- HbA1c Test – No fasting is required for this test.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) – Fast for at least 8 hours, then you will be required to drink a glucose solution provided by the clinic for measurement purposes. The procedure usually takes several hours.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions, inform them of any medications you are taking, and drink enough water before your appointment.
Find Diabetes Tests Near Me / Where to Go for Diabetes Testing?
Why Choose Us?





Navigate Easy With Google Maps
Health Screening Singapore
(Anson House)
Health Screening Singapore
(Camden Medical Centre)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
You can get tested for diabetes in Singapore at a general practitioner clinic or polyclinic using tests such as fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), or oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). At healthscreening.sg, these tests are available from $10.90 for FBG, $27.25 for HbA1c, and $27.25 for OGTT, with consultation fees from $38.15. Subsidies under Screen for Life are also available for eligible individuals. Contact us for more information or to book a same-day appointment.
Most pharmacies in Singapore do not offer full diabetes tests but may sell home blood glucose testing kits for self-monitoring. These kits can give an indication of your blood sugar level but cannot confirm a diagnosis. For comprehensive testing, such as fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), or oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Diabetes in Chinese is written as 糖尿病 and pronounced “táng niào bìng” in Mandarin. The term literally translates to “sugar urine illness,” referring to the excess sugar that can be present in the urine when blood sugar levels are abnormally high.
The cost of a diabetes test in Singapore varies by test type and clinic. At healthscreening.sg, prices start from $10.90 for a fasting blood glucose test, $27.25 for an HbA1c test, and $27.25 for an OGTT, with fasting insulin tests at $66.49. Consultation fees start from $38.15.
Yes, most general practitioners in Singapore can perform or arrange diabetes tests, including fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, and oral glucose tolerance tests. They can also interpret results, recommend follow-up testing if needed, and advise on management or prevention strategies based on your risk profile. At healthscreening.sg, we offer a range of diabetes tests to suit your needs, with subsidies under Screen for Life available for eligible individuals. Contact us for more information or to book an appointment.
You can check your blood sugar at home using a glucometer or home testing kit, which may be purchased from pharmacies. However, these only provide an indication of your current blood sugar level and cannot confirm a diagnosis. A formal diagnosis requires laboratory-based tests such as fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, or OGTT, interpreted by a doctor.
You can request a diabetes test at a general practitioner clinic or polyclinic by explaining your symptoms, risk factors, or family history to the doctor. Mention if you have signs such as increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, or constant tiredness. Your doctor can recommend the most appropriate test, such as fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, or OGTT, and advise on follow-up based on your results.
Diabetes can present with various symptoms, including persistent thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, constant tiredness, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds, recurrent infections, numbness or tingling in the hands or feet, increased hunger, mood changes, dry mouth, itchy skin, darkened skin patches, headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, foot ulcers, vision changes, and irritability. It is advisable to consult a doctor if you notice any combination of these signs.
High blood sugar, or hyperglycaemia, may cause symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, headaches, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. Some people may also experience nausea or unintentional weight loss. These symptoms can develop gradually, and mild cases may go unnoticed. Consulting a doctor can help determine if testing or treatment is required to prevent complications.
The most affordable option is often a fasting blood glucose test, which can cost as little as $10.90 at some clinics. Subsidised screenings are available for eligible Singaporeans and Permanent Residents under programmes like the Health Promotion Board’s Screen for Life (SFL). However, different tests serve different purposes, and the cheapest option may not meet your needs. Consulting a doctor can help determine the most appropriate test for you.
Diabetes testing in Singapore is generally affordable, with costs varying by test type and clinic. At healthscreening.sg, fasting blood glucose tests start from $10.90, HbA1c and OGTT are typically $27.25 each, and fasting insulin tests are about $66.49. Eligible individuals may receive subsidies under the Health Promotion Board’s Screen for Life programme. Contact us for more information or to book an appointment.
Fasting blood glucose, fasting insulin, and oral glucose tolerance tests generally require at least 8 hours of fasting, during which only plain water is allowed. This helps ensure more precise results unaffected by recent food or drink. The HbA1c test does not require fasting. It is advisable to consult a doctor or the testing facility for specific preparation instructions.
Yes, diabetes screening is advised even without a diagnosis, particularly if you are aged 40 or above or have risk factors such as family history, high blood pressure, previous gestational diabetes, or higher body weight. Early testing can detect prediabetes or diabetes, enabling timely treatment and lifestyle changes to prevent progression. If unsure, consult a doctor to determine the appropriate frequency and type of test.
The frequency of blood sugar testing depends on your age, risk profile, and whether you have diabetes. Adults aged 40 and above should be screened at least once every three years, while those at higher risk may require more frequent testing. People with diabetes may need regular home monitoring. It is advisable to consult a doctor for personalised recommendations.
Yes, some routine blood tests may include fasting blood glucose or HbA1c measurements, which can indicate diabetes or prediabetes. However, a formal diagnosis often requires confirmatory testing, such as repeating the test on a separate day or performing an oral glucose tolerance test. Consulting a doctor can help determine which test is most appropriate for your situation.
Diabetes test results are interpreted by comparing your blood sugar levels with standard reference ranges. For example, fasting blood glucose below 6.1 mmol/L is normal, 6.1–6.9 mmol/L suggests prediabetes, and above 6.9 mmol/L on two occasions indicates diabetes. HbA1c results follow similar cut-offs. It is advisable to discuss with your doctor to understand your results in the context of your overall health.


