CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA)
| Test Name | CT Coronary Angiogram |
| Purpose | To detect narrowing or blockages in the coronary arteries and assess the risk of heart disease and heart attack. |
| Test Type | Imaging test (CT scan with contrast dye) |
| Price | From $1,384.30 NETT and inclusive of GST |
| Appointment Options |
Same-day appointment (subject to availability). Book via WhatsApp: 8893 3757 or email: hello@healthscreening.sg |
| Clinic Locations |
Orchard: 1 Orchard
Blvd #05-09 Camden Medical Centre, S248649 Tanjong Pagar: 72 Anson Rd #01-02 Anson House, S079911 |
What Is a CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA) Scan?
A CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA) scan is a non-invasive imaging test used to check if the
coronary arteries are narrowed, blocked, or have other abnormalities that may
increase the risk of chest pain, coronary artery
disease (CAD), or heart attack.
In Singapore, heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death. It is a
serious issue because problems in the coronary arteries often develop silently without
noticeable symptoms. Early detection of narrowing or blockages allows for timely management and
can help reduce the risk of serious complications.

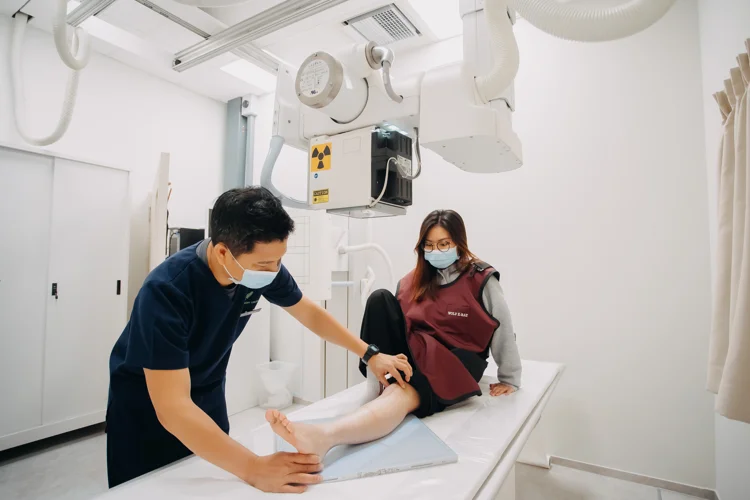
CT Coronary Angiogram Procedure: What to Expect?
A CTCA scan typically involves the following steps:
- An intravenous (IV) line is inserted to deliver contrast dye into your veins, which makes the coronary arteries visible.
- You lie flat on a scanner table while the CT scanner captures rapid X-ray images of the heart. The images are then reconstructed into 3D pictures of the coronary arteries and surrounding blood vessels.
Who Is a CT Coronary Angiogram Usually Recommended for?
You may be advised to undergo a CTCA if you:
- Experience unexplained symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath that may be linked to heart problems
- Have risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, or a family history of heart disease
- Have abnormal or inconclusive findings from earlier cardiac tests, such as an ECG, echocardiogram, or treadmill stress test
- Require a non-invasive alternative to catheter angiography, especially when an invasive procedure is not suitable or carries higher risk

What are Some Risks of CT Coronary Angiogram?
A CTCA is generally well tolerated, but like any medical test it carries some risks:
- Radiation exposure, although typically lower than with conventional angiography. CTCA is usually avoided during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary, as radiation may pose risks to the unborn baby
- Allergic or adverse reactions to contrast dye
- Kidney function concerns in people with pre-existing kidney disease
Your doctor will discuss these risks with you and consider them alongside the potential benefits of CTCA.
How to Interpret Your CT Coronary Angiogram Results?
A CTCA provides detailed images of the coronary arteries, which are reviewed by a radiologist and may also be assessed by a cardiologist. Your doctor will explain the findings in the context of your overall health and risk profile, and advise on any follow-up tests or treatment if needed.

How Much Does CT Coronary Angiogram Cost in Singapore?
At healthscreening.sg, we offer the CT coronary angiogram at our Orchard clinic as part of our cardiovascular assessments and CT scan services, with prices as follows:
| Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| CT Coronary Angiogram | From $1,384.30 |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | $49.05 |
| Treadmill Stress Test with ECG | $218 |
| 2D Echocardiogram | $436 |
| Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test | $163.50 |
| CT Calcium Score Test | $403.30 |
*Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST.
^Prices last updated on
Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
How Long Does a CT Coronary Angiogram Take?
A CTCA appointment usually takes about 30 to 60 minutes during off-peak hours at our
clinic. The scan itself lasts only a few seconds, but additional time is needed for registration and
preparation. Your doctor will review the results with you after the scan.
Contact us to find the most suitable time to schedule
your appointment.
How to Prepare for Your CT Coronary Angiogram?
Before undergoing a CTCA, you should avoid caffeinated drinks and exercise for at least 12 hours before your appointment. Follow any additional preparation instructions provided by your doctor or the clinic staff.
How to Book a CT Coronary Angiogram?
Why Choose Us?







Navigate Easy With Google Maps
Health Screening Singapore (Anson House)
Nearest MRT: EW15 Tanjong PagarHealth Screening Singapore (Camden Medical Centre)
Nearest MRT: TE13 Orchard BoulevardHealth Screening Singapore (CPF Jurong Building)
Nearest MRT: NS1/EW24 Jurong EastFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A coronary angiogram is an imaging test that uses X-rays and contrast dye to visualise blood flow in the coronary arteries, while cardiac catheterisation is the broader procedure in which a catheter is inserted into the heart for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, such as angioplasty or stent placement. In practice, a coronary angiogram is one of the diagnostic tests performed during cardiac catheterisation.
An angiogram is a diagnostic test that uses contrast dye and imaging to detect blockages or narrowing in blood vessels, while angioplasty is a treatment procedure that uses a balloon or stent to widen narrowed arteries. Angiograms may be performed first to confirm blockages, and angioplasty may follow if intervention is needed.
A CT coronary angiogram is not generally considered painful, as it is non-invasive and involves lying still in a CT scanner while images are taken. Patients may feel mild discomfort from the insertion of an IV line for contrast dye or a warm sensation when the dye enters the bloodstream. These effects are usually brief and well tolerated. It is advisable to consult a doctor if you have concerns about the procedure or possible side effects.
Coronary angiogram in Chinese is 冠状动脉造影 (guānzhuàng dòngmài zàoyǐng), which literally means "coronary artery imaging." It describes the diagnostic procedure that evaluates narrowing or blockages in the coronary arteries.
A doctor may order a CT coronary angiogram to check for narrowed or blocked coronary arteries in patients with chest pain, shortness of breath, or inconclusive findings from other cardiac tests such as an ECG, echocardiogram, or treadmill stress test. It may also be used to assess risk in patients with multiple risk factors for heart disease or as a non-invasive alternative to catheter angiography.
Angiogram results do not have a fixed validity period because artery narrowing or blockages can progress over time. The findings reflect the condition of the coronary arteries at the time of the test, but changes may occur months or years later depending on risk factors and lifestyle. Doctors may recommend repeat testing if new symptoms develop or if risk factors worsen.
At healthscreening.sg, a CT coronary angiogram costs from $1,384.30 NETT inclusive of GST, excluding consultation fees. The final amount may vary depending on whether additional cardiac tests are recommended. Consult us directly for an accurate estimate tailored to your medical needs or to book an appointment.
If an angiogram shows a blockage, your doctor or cardiologist will assess its severity and location to decide on the next steps. Minor blockages may be managed with medication and lifestyle changes, while significant ones could require procedures such as angioplasty with stent placement or, in some cases, bypass surgery. The appropriate treatment depends on overall heart health, symptoms, and risk factors.
A coronary angiogram can vary in duration depending on whether it is performed as a CT coronary angiogram (CTCA) or an invasive catheter angiogram. A CTCA scan itself takes only a few seconds, with the entire clinic visit usually lasting 30 to 60 minutes including preparation. An invasive angiogram typically takes 30 minutes to an hour, with total hospital time longer due to preparation, monitoring, and potential interventions such as angioplasty. It is advisable to check with your healthcare provider for a more accurate estimate.
Heart blockages can sometimes be evaluated using non-invasive tests such as a CT coronary angiogram, echocardiogram, treadmill stress test, or CT calcium scoring. These methods provide useful information on heart function and artery health without catheter insertion. However, while these tests are valuable for screening and diagnosis, an invasive coronary angiogram, or catheter angiography, remains the gold standard for detailed assessment. Consulting a cardiologist can help determine the most appropriate test based on your symptoms and risk profile.
A CT angiogram is a non-invasive test using CT imaging and contrast dye to create 3D images of the coronary arteries, while a regular angiogram, or catheter angiography, involves inserting a catheter directly into the arteries to inject dye and take X-ray images. CT angiograms are useful for diagnosis and risk assessment, whereas catheter angiography may allow for treatment, such as angioplasty, during the same procedure.
Three common risks of an angiogram, which refers to the invasive catheter-based procedure and not a CT coronary angiogram (CTCA), include bleeding or bruising at the catheter insertion site, allergic reactions to contrast dye, and kidney complications in patients with pre-existing kidney issues. Less common risks include irregular heart rhythms or blood vessel damage. While serious complications are rare, your doctor will discuss whether the potential risks outweigh the benefits in your case.
For an invasive catheter-based procedure and not a CT coronary angiogram (CTCA), arteries generally begin healing within a few days. Most patients are advised to avoid strenuous activity for about a week. Recovery may vary depending on whether access was through the wrist or groin, with groin entry sometimes requiring a longer healing period. It is advisable to check with your doctor or cardiologist for an estimate tailored to your condition.
The scan commonly used to detect blocked arteries is a CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA), which produces detailed images of the coronary arteries to identify narrowing, blockages, or atherosclerosis. Unlike an invasive angiogram, CTCA is non-invasive and uses contrast dye with a CT scanner. In some cases, other imaging tests such as stress echocardiograms or CT calcium scoring may be recommended.
The abbreviation CTCA stands for CT Coronary Angiogram, a non-invasive imaging test that uses computed tomography (CT) and contrast dye to assess the coronary arteries. The scan helps detect narrowing, plaque, or blockages that may increase the risk of chest pain, coronary artery disease, or heart attack. CTCA may be advised for patients with symptoms or risk factors where detailed imaging is needed to guide diagnosis and treatment decisions.
