Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Singapore
| Continuous Glucose Monitoring Option | Abbott FreeStyle Libre Sensor |
| Purpose | Monitors glucose levels continuously throughout the day and night, providing real-time data to guide diabetes care and treatment adjustments. |
| Recommended For | People living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who need detailed, ongoing glucose tracking, as well as those with unstable or frequently changing blood sugar levels. |
| Price | $27.25 NETT (first sensor for first-time users) |
| Appointment Options |
Same-day appointment (subject to availability). Book via WhatsApp: 8893 3757 or email: hello@healthscreening.sg |
| Clinic Locations |
Orchard: 1 Orchard Blvd
#05-09 Camden Medical Centre, S248649 Tanjong Pagar: 72 Anson Rd #01-02 Anson House, S079911 |
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring?
Continuous glucose monitoring, or CGM, is a system that tracks glucose levels in real time
throughout the day and night using a wearable sensor. The device measures glucose in the body continuously,
providing round-the-clock insights without the need for frequent finger-prick testing.
By automatically recording readings, CGM allows you to see how factors such as meals, exercise,
stress, and medication affect your glucose levels. This ongoing feedback can support more
effective daily diabetes management and help with maintaining stable long-term glucose control.
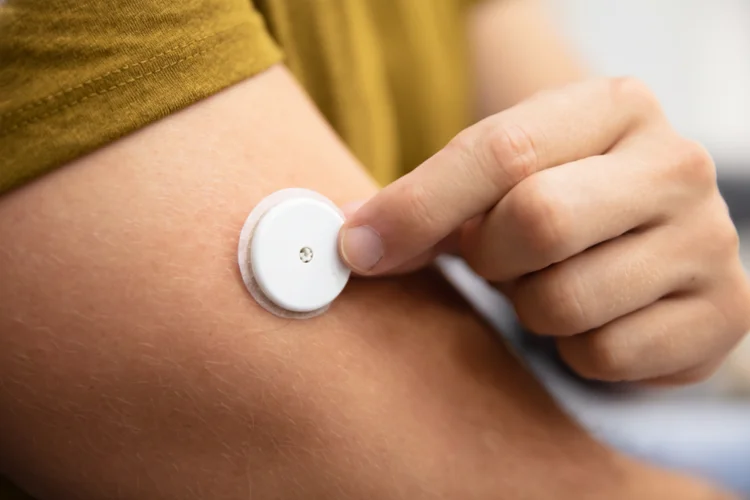
How Does Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems Work?
Continuous glucose monitoring functions by detecting glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which is the fluid surrounding the body's cells, through a small sensor placed under the skin. The process typically involves several steps:
- Sensor placement – The sensor is inserted beneath the skin, usually on the upper arm or abdomen. Most CGM systems are designed for self-application using a built-in applicator.
- Measurement – Glucose levels in the interstitial fluid are assessed at regular intervals.
- Wireless transmission – Readings are sent wirelessly to a display device, smartphone, or insulin pump.
- Live updates – Glucose values are refreshed every few minutes, allowing continuous visibility of trends.
- Alerts and notifications – The system can sound an alarm if glucose levels rise above or fall below preset limits.
- Routine replacement – Each sensor has a limited lifespan and needs regular replacement to maintain accuracy. Some systems also require transmitter changes after a few months.
Who Might Continuous Glucose Monitoring Be Suitable For?
Continuous glucose monitoring is particularly useful for individuals who need close and consistent tracking of their blood glucose. It is commonly recommended for:
- People with type 1 diabetes, as they depend on insulin and benefit from real-time data to adjust their dosage precisely.
- Individuals with type 2 diabetes who use insulin or experience wide fluctuations in glucose levels, since CGM helps tailor lifestyle and treatment plans more effectively.
- Those with hypoglycaemia unawareness, where low blood sugar episodes occur without warning symptoms, allowing alerts before levels become dangerous.
- Children and teenagers living with diabetes, where CGM enhances the safety of glucose monitoring by reducing the risk of unnoticed highs or lows, especially overnight or during school hours.

Key Advantages of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring offers several key advantages, including:
1. Reduced Need for Finger-Prick Testing
CGM greatly reduces the need for multiple daily finger-prick checks, making glucose
monitoring more comfortable and less intrusive.
2. Adjustable Alerts for Glucose Changes
You can set individual glucose thresholds so that alerts are triggered when your levels
go too high or too low, helping you respond quickly to prevent complications.
3. Real-Time Glucose Trends
Data is updated automatically every few minutes and displayed as easy-to-read graphs,
showing whether glucose levels are stable, increasing, or decreasing over time.
4. Personalised Insights for Daily Habits
Regular trend analysis helps you understand how food, exercise, and sleep affect your
glucose levels. These insights can then be reviewed with your doctor to fine-tune your
management plan.
What Types of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems Are Available?
Two main types of continuous glucose monitoring systems are available: real-time CGM and flash glucose monitoring (FGM). Both rely on replaceable sensors, though their data access methods differ.
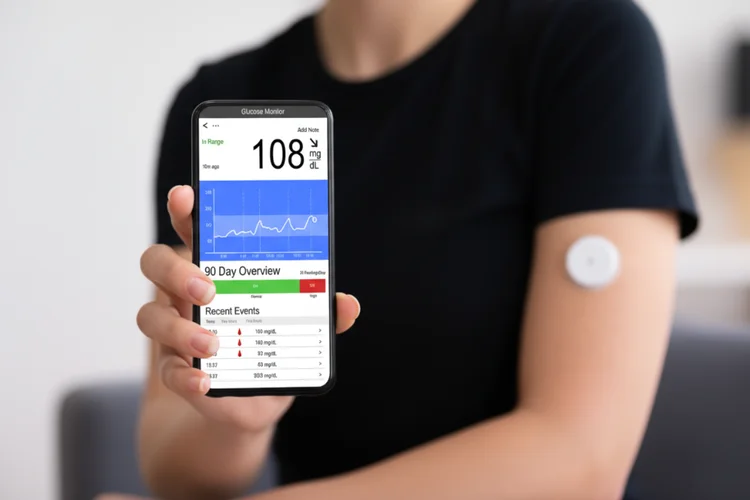
| Type of Monitoring System | Description and Key Details |
|---|---|
| Real-time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) |
Provides automatic, continuous glucose readings that are displayed directly on a compatible
smartphone or receiver.
|
| Flash Glucose Monitoring (FGM) |
Measures glucose continuously but requires scanning the sensor with a reader or smartphone
to view data.
|
What Are Some Limitations of Continuous Glucose Monitoring?
Although CGM systems offer valuable benefits, some practical limitations should be recognised:
- Accuracy variations – Because CGM tracks glucose in interstitial fluid rather than directly in the bloodstream, readings may lag during rapid changes, such as after meals or exercise. Finger-prick confirmation is still recommended in these instances.
- Ongoing costs – Regular sensor and occasional transmitter replacements contribute to the long-term cost of using the system.
- Skin sensitivity – Mild irritation, itching, or redness may develop at the site of sensor insertion.
Despite these drawbacks, many individuals find CGM an important tool for maintaining stable glucose control and preventing complications, particularly when incorporated into a care plan guided by your doctor.
How Much Does Continuous Glucose Monitoring Cost in Singapore?
At healthscreening.sg, continuous glucose monitoring is offered alongside a range of diabetes-related tests and management services at the following prices:
| Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Abbott FreeStyle Libre Sensor | $27.25 (first sensor for first-time users) |
| Diabetes Testing | |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Test | $10.90 |
| Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) Test | $27.25 |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) | $27.25 |
| Fasting Insulin Test | $66.49 |
| [Optional] Mobile Blood Drawing Service | $54.50 (per location up to 5 pax) |
| Screen for Life Diabetes Screening | $0 to $5 (depending on CHAS/MG/PG status) |
*Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST.
Currently, the Dexcom CGM system is eligible for subsidy under Singapore's public healthcare schemes
for individuals with type 1 diabetes, with up to 80% of the cost covered. Other CGM devices do
not receive national healthcare subsidies at this time.
Maintaining consistent glucose monitoring supports healthier ageing and helps prevent complications
associated with diabetes. In addition to CGM, we also provide comprehensive health screening and
longevity assessments to promote overall wellbeing
and assist in managing long-term health goals.
Book an Appointment for Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Why Choose Us?







Navigate Easy With Google Maps
Health Screening Singapore
(Anson House)
Health Screening Singapore
(Camden Medical Centre)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The cost of continuous glucose monitoring devices in Singapore varies depending on the model and replacement schedule. Some systems, such as Dexcom for type 1 diabetes, may be subsidised at public healthcare institutions. At healthscreening.sg, we provide the Abbott FreeStyle Libre sensor from $27.25 for first-time users, and our doctors can provide ongoing support for diabetes care and long-term management.
Some continuous glucose monitoring devices, such as Dexcom, can be purchased from authorised providers or pharmacies in Singapore without a prescription. While they can be used independently, integrating CGM into your diabetes care under a doctor's supervision allows for more accurate interpretation of readings and more medically guided management of your condition. At healthscreening.sg, the Abbott FreeStyle Libre sensor is available from $27.25 for first-time users.
Inserting a CGM sensor usually causes only mild, brief discomfort similar to a small pinch, as the device sits just under the skin. Modern applicators are designed for quick and simple placement, and most users find the process tolerable after initial use. Minor skin irritation may occur at the insertion site but typically resolves quickly. If discomfort persists, it is best to consult your doctor for guidance.
Continuous glucose monitors are widely recognised as useful tools for tracking glucose trends and supporting diabetes management. They measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, providing real-time data that helps identify patterns and fluctuations. However, finger-prick tests may still be needed during rapid changes or to confirm readings. The accuracy of CGM systems depends on proper use and calibration, where required.
While CGM systems reduce the need for frequent finger-prick testing, they do not completely eliminate it. Finger-prick tests may still be necessary in certain situations, such as confirming rapidly changing readings or calibrating specific devices. Continuous glucose monitoring provides ongoing insights, but blood glucose testing remains an important reference for accuracy and treatment decisions. Always follow your doctor's recommendations on monitoring methods.
The main drawbacks of CGM systems include cost, the need for regular sensor replacement, and occasional skin irritation at the insertion site. Readings can also lag slightly behind actual blood glucose levels during rapid changes, such as after eating or exercising. Despite these limitations, many users find CGM valuable for maintaining better glucose control, particularly when used with regular medical review and support.
An Apple Watch cannot directly measure blood sugar levels, as it lacks a glucose sensor. However, it can display glucose data from compatible continuous glucose monitoring systems, such as Dexcom or FreeStyle Libre, when paired via an app. This allows users to view readings, trends, and alerts conveniently on their wrist. Always ensure the connected CGM device is properly calibrated and used according to your doctor's guidance.
A continuous glucose monitor is not intended to diagnose prediabetes but can help observe glucose patterns once the condition has been identified. Prediabetes is typically confirmed through blood tests such as fasting glucose, HbA1c, or an oral glucose tolerance test. CGM can still offer helpful insights into how diet and physical activity affect glucose levels. If you suspect prediabetes or have risk factors, it is advisable to consult a doctor for proper screening.
Most continuous glucose monitoring sensors are water-resistant and can be worn while showering, swimming, or exercising. However, prolonged submersion or exposure to very hot water may affect adhesion or sensor performance. It is important to follow the manufacturer's care instructions for your specific device. If a sensor becomes loose or stops transmitting data after water exposure, consult your doctor or replace the sensor as advised.
The needle used during CGM sensor insertion does not stay in the body. It is only used to guide the tiny filament, or sensor wire, beneath the skin, after which the needle is withdrawn. The soft filament remains in place to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. This design minimises discomfort during wear. If you experience persistent pain or irritation, it is advisable to consult your doctor.
In Singapore, continuous glucose monitoring devices such as Dexcom and FreeStyle Libre can be purchased from authorised providers or pharmacies without a prescription. While they can be used independently, starting CGM with medical guidance allows for correct setup and accurate interpretation of readings within a structured care plan. At healthscreening.sg, the Abbott FreeStyle Libre sensor is available from $27.25 for first-time users, supporting ongoing diabetes monitoring and management.
The lifespan of a continuous glucose monitoring sensor varies depending on the device. Most real-time CGM sensors, such as Dexcom, last about 10 days, while flash glucose monitoring sensors like FreeStyle Libre can last up to 14 days. After this period, the sensor must be replaced to maintain accuracy. Always follow the manufacturer's recommended replacement schedule and your doctor's instructions for optimal monitoring.
