2D Echocardiogram
| Test Name | 2D Echocardiogram |
| Purpose | To assess heart structure, pumping function, and blood flow, and to detect conditions such as valve problems, congenital heart defects, or signs of heart failure. |
| Test Type | Imaging test (ultrasound of the heart) |
| Price | $436 NETT and inclusive of GST |
| Appointment Options |
Same-day appointment (subject to availability). Book via WhatsApp: 8893 3757 or email: hello@healthscreening.sg |
| Clinic Locations |
Orchard: 1 Orchard
Blvd #05-09 Camden Medical Centre, S248649 Tanjong Pagar: 72 Anson Rd #01-02 Anson House, S079911 |
What Is a 2D Echocardiogram?
A 2D echocardiogram, sometimes called a 2D echo, is a non-invasive
ultrasound test that uses sound waves to
create real-time images of the heart and its structures. It shows the heart’s
chambers, valves, walls, and blood flow, helping doctors evaluate how well the heart is
functioning.
Because it provides moving images, a 2D echocardiogram is often referred to as a heart
ultrasound or cardiac ultrasound.

How Does a 2D Echocardiogram Work?
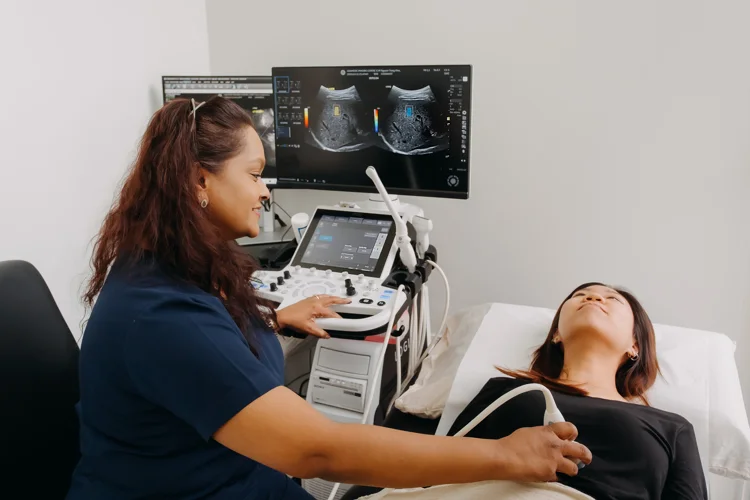
A 2D echocardiogram works by using high-frequency sound waves sent through a handheld device called a transducer, which is placed on the chest. The sound waves bounce off the heart structures and are converted into two-dimensional moving images on a monitor. This allows the heart’s pumping action, valve movement, and blood flow to be observed in real time.
What Can a 2D Echocardiogram Detect?
A 2D echocardiogram can detect structural problems, functional abnormalities, and signs of disease affecting the heart. It may reveal:
- Reduced pumping function of the heart
- Narrowing or leakage of heart valves
- Enlargement or thickening of heart chambers
- Congenital heart defects present from birth
- Evidence of cardiomyopathy
- Blood clots, tumours, or fluid around the heart

When Is a 2D Echocardiogram Usually Recommended?
A 2D echocardiogram may be recommended as part of a non-urgent assessment when there are concerns about heart function or cardiovascular risk. It is often considered in the following situations:
- Further evaluation of heart murmurs (first detected during a physical examination) or irregular rhythms noted on an ECG
- Monitoring of people with long-term risk factors such as high blood pressure or diabetes that may affect the heart over time
- Follow-up in individuals with a previous diagnosis of heart disease or a history of stroke to assess ongoing heart function
- Part of a comprehensive health screening for those with cardiovascular risk factors
How Is a 2D Echocardiogram Performed?
A 2D echocardiogram is usually carried out in the following steps:
- You will lie on an examination bed while gel is applied to your chest.
- A transducer is moved across different areas of the chest to capture images from several angles.
- You may be asked to change position or hold your breath briefly to improve image quality.

Are There Any Risks to a 2D Echocardiogram?
A 2D echocardiogram is a non-invasive test and is widely regarded as low risk with no exposure to radiation. Some people may feel mild discomfort from the pressure of the transducer on the chest, but this is temporary. You can usually return to your normal activities immediately afterwards.
How Is a 2D Echocardiogram Different from Other Heart Tests?
A 2D echocardiogram provides real-time images of the heart’s structure (chambers and valves) and function (pumping action and blood flow), while other cardiovascular tests assess electrical activity, arterial health, or detailed imaging in different ways.
| Test | What It Measures | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Records the heart’s electrical activity | Detects rhythm irregularities, previous heart attacks, and conduction problems |
| Stress Test (with ECG) | Monitors heart performance during exercise or medication-induced stress | Assesses how the heart responds to physical strain and detects reduced blood flow |
| CT Calcium Score | Measures calcified plaque in the coronary arteries using CT scanning | Evaluates risk of coronary artery disease by detecting early calcification |
| Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test | Measures thickness of the carotid artery walls using ultrasound | Detects early signs of atherosclerosis and monitors arterial health |
| CT Coronary Angiography (CTCA) | Visualises blood flow in coronary arteries using a CT scan with contrast dye | Identifies narrowing or blockages in the coronary arteries |
How Much Does a 2D Echocardiogram Cost in Singapore?
At healthscreening.sg, we provide the 2D echocardiogram test as part of our range of cardiovascular assessments, with the prices as follows:
| Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| 2D Echocardiogram | $436 |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | $49.05 |
| Treadmill Stress Test with ECG | $218 |
| CT Calcium Score Test | $403.30 |
| Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test | $163.50 |
| CT Coronary Angiogram | From $1,384.30 |
*Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST.
^Prices last updated on
Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
Our 2D echocardiogram test is carried out at a cardiologist’s clinic and the results will be reviewed by
a cardiologist.
How Long Does a 2D Echocardiogram Take?
A 2D echocardiogram typically takes about 30 to 60 minutes from arrival to completion
during off-peak hours. For guidance on the best time to schedule your appointment, please contact us.
Your test results will be reviewed and sent to you by email within 3 working days.
Results may indicate normal heart function or reveal conditions that require further evaluation. If
abnormalities are detected, your doctor may recommend additional tests or treatments tailored to your
needs.
Do I Need to Prepare for a 2D Echocardiogram?
No special preparation is needed for a 2D echocardiogram. You may eat, drink, and take your usual medications before the test. If any specific instructions apply to your case, the clinic will let you know in advance.
How to Book an Appointment for A 2D Echocardiogram?
Why Choose Us?







Navigate Easy With Google Maps
Health Screening Singapore (Anson House)
Nearest MRT: EW15 Tanjong PagarHealth Screening Singapore (Camden Medical Centre)
Nearest MRT: TE13 Orchard BoulevardHealth Screening Singapore (CPF Jurong Building)
Nearest MRT: NS1/EW24 Jurong EastFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
An ECG records the heart’s electrical signals and helps detect rhythm disturbances, conduction problems, or evidence of previous heart attacks. In contrast, a 2D echo uses ultrasound to produce moving images that show the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow. The two tests are complementary, as the ECG evaluates electrical activity while the 2D echo assesses the heart’s structure and pumping function.
A normal 2D echo result generally indicates that the heart’s structure and pumping function appear within expected ranges. However, it does not completely rule out all heart conditions, as some electrical or vascular issues may not be detected by ultrasound. It is advisable to discuss your results with your doctor or cardiologist, who can interpret them in the context of your overall health, symptoms, and risk factors.
A 2D echo cannot directly show blockages in the coronary arteries but may indicate secondary effects, such as reduced pumping efficiency or abnormal heart wall motion. Other investigations, including CT calcium scoring, CT coronary angiography, or stress testing, are more suitable for detecting arterial blockages. It is advisable to consult a doctor or cardiologist to determine which test is most appropriate for your situation.
A 2D echocardiogram can show abnormalities such as enlarged heart chambers, reduced pumping function, narrowing or leakage of heart valves, congenital heart defects, and fluid around the heart. It may also detect other issues, including blood clots, tumours, or signs of cardiomyopathy, depending on the individual’s condition.
A 2D echocardiogram is not the first-line test for diagnosing urgent heart failure, unlike blood tests such as B-type natriuretic peptide, an ECG, or a chest X-ray, which are commonly used in emergency settings. Once the condition is stabilised, a 2D echo may be used to assess pumping function, chamber size, and valve movement, helping to confirm the diagnosis and guide management. If you develop sudden chest pain, severe breathlessness, or swelling, you should go to the Accident & Emergency department immediately.
A 2D echocardiogram provides important insights that can support the diagnosis of conditions such as valve disease, congenital heart defects, cardiomyopathy, fluid around the heart, and reduced heart function. It is also useful for monitoring known heart conditions and assessing treatment response. However, it may not be sufficient to diagnose all cardiovascular problems on its own, and further tests are often required.
A 2D echo does not require fasting, and you can eat, drink, and take your regular medications before the test. Unlike some imaging procedures that may need dietary restrictions, a standard 2D echocardiogram is performed without special preparation. If specific instructions apply due to your individual condition or if other tests are scheduled together, our clinic will inform you in advance.
A 2D echocardiogram may be recommended to evaluate heart structure, pumping function, or blood flow when there are symptoms, risk factors, or findings that suggest possible heart problems. It can help investigate heart murmurs, assess valve function, or monitor existing conditions such as high blood pressure or a history of heart disease.
For a 2D echo, you may need to remove clothing from the upper body so the technician can place the ultrasound probe directly on the chest. A gown or covering is usually provided for comfort and privacy. This allows clear images to be taken, as fabric or thick layers can interfere with sound waves. The process is non-invasive and is carried out in a dedicated examination room.
Yes, you can usually drive yourself home after a 2D echocardiogram. The test does not involve sedation, medication, or procedures that impair concentration or physical ability. You can return to your normal daily activities, including driving, work, or exercise, immediately after the appointment unless advised otherwise due to other ongoing medical concerns.
The term “normal echocardiogram” usually refers to standard transthoracic echocardiography, and 2D echocardiography is the most common type used in this setting. A 2D echo produces real-time, two-dimensional images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and pumping function. Other specialised echocardiograms, such as 3D or stress echocardiography, provide additional information in specific clinical situations.
A 2D echocardiogram provides insights into the heart’s structure and function that may help identify valve abnormalities, congenital heart defects, cardiomyopathy, or fluid around the heart. It can also show changes in chamber size, wall motion, or blood flow that suggest underlying disease. However, it is not the first-line test for certain conditions, and additional investigations are often required to confirm a diagnosis.
