Oral Contraceptive Pill Singapore
What Are Oral Contraceptives?
Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs), commonly known as birth control pills, are medications that
prevent pregnancy by regulating hormone levels involved in ovulation and the menstrual
cycle. These pills typically contain synthetic forms of oestrogen and progestin, or
progestin alone.
OCPs provide continuous contraceptive protection when taken daily. In comparison, emergency
contraception (commonly called the morning-after pill) is taken
after unprotected sex to reduce the likelihood of pregnancy. Period delay pills, which contain
progestin, can temporarily postpone menstruation but do not offer contraceptive protection.

How Do Oral Contraceptives Work?
Oral contraceptives prevent pregnancy by altering hormone levels to interfere with ovulation, fertilisation, and implantation.
- Suppressing Ovulation – Stable levels of synthetic oestrogen and progestin inhibit the surge in luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) that is needed to trigger egg release.
- Blocking Sperm Movement – Progestin thickens the cervical mucus, making it more difficult for sperm to travel through the cervix to reach the egg.
- Changing the Uterine Lining – The endometrial lining becomes thinner, making it less suitable for a fertilised egg to implant.
Types of Oral Contraceptives
Combined Oral Contraceptive Pills (COCPs)
Combined oral contraceptive pills contain both oestrogen and progestin and primarily function by inhibiting ovulation. There are various formulations available:
- Monophasic Pills – Each active pill contains the same hormone dose, providing consistent hormone levels throughout the cycle.
- Multiphasic Pills – Hormone doses vary at different points in the cycle to better simulate natural hormonal fluctuations. This may reduce breakthrough bleeding and side effects.
- Extended-Cycle Pills – Designed to reduce the frequency of menstruation, these allow users to experience withdrawal bleeding only every few months, beneficial for those with painful or heavy periods.

Other Uses of Oral Contraceptive Pills
Beyond birth control, oral contraceptive pills are frequently used to manage a variety of hormone-related health conditions. Their non-contraceptive benefits differ depending on the specific formulation and individual health concerns. Common uses include:
- Menstrual Regulation – Helps stabilise menstrual cycles, relieve cramping (dysmenorrhoea), and lighten heavy bleeding (menorrhagia).
- Premenstrual Symptoms – May ease premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) symptoms by maintaining steadier hormone levels.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – Can aid in regulating periods and lowering androgen levels, which may improve acne and reduce hirsutism (excess facial or body hair).
- Endometriosis Management – May reduce pelvic discomfort by preventing ovulation and limiting the growth of endometrial tissue.
- Menstrual-Related Migraines – Continuous-use regimens may help prevent hormonal fluctuations that trigger migraines.
These uses should be guided by a doctor, as oral contraceptives may not be suitable for everyone depending on individual medical history and risk factors.
Potential Side Effects of Oral Contraceptive Pills
Most people tolerate oral contraceptives well, but some may experience temporary side effects while adjusting to the hormonal changes. Common effects include:
- Nausea and Headaches – These can occur early in the adjustment period due to hormone sensitivity.
- Bloating and Breast Tenderness – May result from fluid retention or hormonal shifts.
- Mood Changes – Hormones can influence mood-regulating chemicals like serotonin.
- Breakthrough Bleeding – Light spotting may occur, especially in the initial months of use.
Though uncommon, some serious risks are associated with oral contraceptives. These may include venous thromboembolism (VTE), stroke, heart attack, elevated blood
pressure, or worsening of existing hypertension, particularly in individuals with cardiovascular risk
factors such as smoking, heart disease, or a history of blood clots.
If side effects persist or cause concern, speak
with a doctor to explore alternative contraceptive options.
How Much Do Oral Contraceptives Cost?
At healthscreening.sg, we provide access to a variety of contraceptive and hormone-related services. Our services and pricing include:
| Test/Treatment | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| Teleconsultation | From $38.15 |
| Medication | |
| Birth Control Pill (Yaz®) | $43.60 (per box of 40 tablets) |
| Emergency Contraceptive Pill (Ella®) | $43.60 |
| Period Delay Pill - Noresthisterone | $0.76 per tab |
| Hormone Tests | |
|
Amenorrhoea (Hormone) Profile 3 Testosterone, Estradiol (E2), Free T4, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinising Hormone (LH), Prolactin This test is recommended for individuals with irregular menstrual bleeding and should be conducted between days 2 to 5 of the menstrual cycle for optimal results. |
$130.80 |
|
Female Acne/Weight Gain Screen** Testosterone, Estradiol, Progesterone, TSH, Cortisol, FSH, LH, Prolactin, DHEAS, SHBG This test is recommended for individuals with suspected hormonal acne and should be conducted between days 2 to 5 of the menstrual cycle for optimal results. |
$218 |
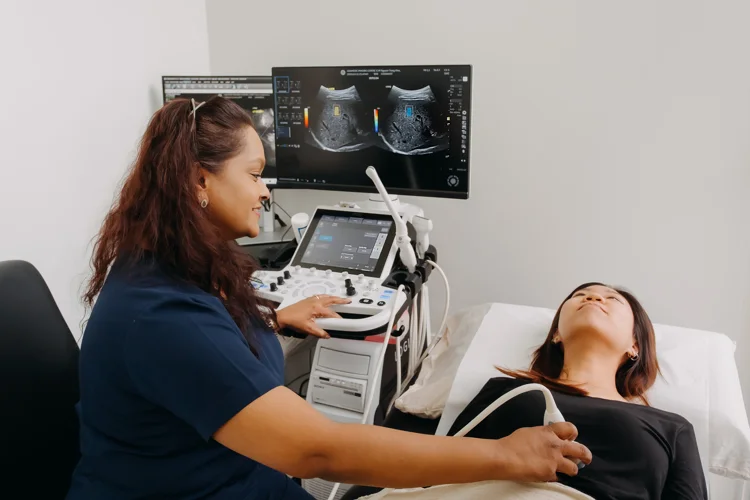
| Ultrasound | |
| Ultrasound Pelvis (Transabdominal) | $207.10 |
| Ultrasound Pelvis (Transvaginal) | $207.10 |
*Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST.
**Test must be done between 8:30 AM and 10:00 AM for accuracy.
Hormone testing packages are also available. Contact
us for more information.
How to Use Oral Contraceptive Pills?
To maintain effectiveness, take the pill at the same time each day. The regimen depends on the pack type:
21-Day Pack
- Take 1 active pill daily for 21 days.
- Stop for 7 days (no pills taken) to allow withdrawal bleeding.
- Resume with the next pack on the 8th day, even if bleeding hasn’t ended.
28-Day Pack
- Take 1 pill daily for 28 days.
- The last 4 to 7 pills are inactive (placebo), leading to withdrawal bleeding.
- Begin the next pack immediately after finishing the previous one.
If starting outside the first 5 days of your cycle, use an additional contraceptive method for the first
7 days.
When switching from another method (e.g. patch, injection, implant), seek medical advice from your
doctor for proper timing to avoid gaps in protection.
What Happens if I Missed a Dose?
Missing pills can affect contraceptive protection, especially if delays exceed 12 hours. Follow these recommendations for combined pills:
Less than 12 hours late:
- Take the missed pill as soon as you remember.
- Continue the next pill at the usual time (means taking 2 pills in one day).
- No extra contraception is needed.
More than 12 hours late:
If you missed a pill after 12 hours, follow this guide based on the week of your pack:
| Week | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Week 1 |
|
| Week 2 |
|
| Week 3 |
|
Important: Vomiting or severe diarrhoea within 3 to 4 hours of taking a pill may reduce
its effectiveness. It should be treated as a missed dose.
When in doubt, refer to the specific pill packaging instructions or consult your doctor for medical
advice.
Where to Get Oral Contraceptive Pills in Singapore?
Why Choose Us?







Navigate Easy With Google Maps
Health Screening Singapore (Anson House)
Nearest MRT: EW15 Tanjong PagarHealth Screening Singapore (Camden Medical Centre)
Nearest MRT: TE13 Orchard BoulevardHealth Screening Singapore (CPF Jurong Building)
Nearest MRT: NS1/EW24 Jurong EastFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Yes, most oral contraceptive pills prevent ovulation by regulating hormone levels. Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) maintain steady levels of synthetic oestrogen and progestin, which suppress the hormonal surge of luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) needed to release an egg. Progestin-only pills (POPs) mainly work by thickening cervical mucus and modifying the uterine lining, making it more difficult for fertilisation and implantation to occur.
You can start oral contraceptive pills using different approaches based on personal preference and your doctor’s advice. Starting on the first day of your period offers immediate protection. The “Sunday start” method begins on the Sunday after your period starts and requires backup contraception for the first 7 days. The “quick start” method allows you to begin at any point in your cycle, but additional contraception is needed for 7 days unless started within the first 5 days of menstruation. If you are unsure, it is best to consult your doctor for personalised medical advice.
While long-term use is generally well tolerated, it may increase the risk of conditions such as venous thromboembolism (VTE), stroke, or high blood pressure. These risks are higher in individuals with certain risk factors like smoking, obesity, or cardiovascular disease. It is advisable to consult a doctor to evaluate whether oral contraceptives are suitable based on your medical history and health profile.
Yes, smoking increases the risk of cardiovascular side effects when using oral contraceptives, especially combined pills. The risk of blood clots, stroke, or heart attack is notably higher in individuals over 35 who smoke more than 15 cigarettes a day. Always consult a doctor to determine the most appropriate contraceptive method based on your health and lifestyle.
Most individuals tolerate oral contraceptive pills well, but some may experience temporary side effects such as nausea, headaches, breast tenderness, bloating, spotting, or mood changes. In certain individuals, particularly those with cardiovascular risk factors, they may increase the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), stroke, or high blood pressure. A consultation with a doctor can help assess whether the pill is appropriate for your needs.
In addition to preventing pregnancy, oral contraceptives can offer several health benefits. These include regulating menstrual cycles, reducing period pain, and making bleeding lighter. They are also used to manage medical conditions such as PCOS, endometriosis, and hormonal acne. The specific benefits vary based on your health goals and should be discussed with a doctor.
Oral contraceptives work by disrupting three key processes: ovulation, sperm movement, and implantation. Combined oral contraceptive pills (COCs) suppress the hormone surge needed to release an egg. Progestin-only pills (POPs) primarily act by thickening cervical mucus, making it harder for sperm to reach the egg. Both types also thin the uterine lining, reducing the chance of a fertilised egg implanting.
Combined oral contraceptive pills (COCs) contain synthetic oestrogen and progestin and work by preventing ovulation, thickening cervical mucus to block sperm, and altering the uterine lining to reduce the likelihood of implantation. These combined actions help prevent pregnancy when the pill is taken consistently as directed.
At healthscreening.sg, a box of birth control pills (Yaz®) costs $43.60 for 40 tablets. Emergency contraceptive pills are also priced at $43.60. Period delay pills containing norethisterone cost $0.76 per tablet. Consultation fees begin at $38.15 for teleconsultations and $49.05 for in-clinic visits. All fees are NETT and include GST.
No, oral contraceptive pills require a doctor’s prescription in Singapore and are not available over the counter. A consultation is necessary to determine the appropriate type based on your health. At healthscreening.sg, we provide same-day appointments and offer various contraceptive options, including oral contraceptives at $43.60 per box.
At healthscreening.sg, contraceptive pills are available at $43.60 per box (40 tablets). Emergency contraception is priced the same. Period delay pills are $0.76 per tablet. Consultation fees start from $38.15 for teleconsults and $49.05 for in-person visits, with all charges inclusive of GST.
Yes, a prescription from a general practitioner (GP) is required to obtain oral contraceptives in Singapore. The doctor will assess your health to determine if the pill is suitable for you. At healthscreening.sg we offer same-day appointments for oral contraceptives, emergency contraception, and period delay pills.
To access contraception in Singapore, you must first consult a doctor. The doctor will review your medical history and recommend a suitable contraceptive method based on your health and lifestyle. At healthscreening.sg, we offer consultations and same-day access to birth control pills, emergency contraceptive pills, and period delay options. Contact us for more information.
Common side effects of oral contraceptive pills include nausea, headaches, bloating, breast tenderness, mood fluctuations, and spotting. These symptoms often subside with continued use. However, the pills may also carry a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), stroke, or high blood pressure, especially in individuals with pre-existing risk factors. If you are concerned about side effects, speak to a doctor for personalised advice.
