CT Calcium Score Test
| Test Name | CT Calcium Score Test |
| Purpose | Measures calcified plaque in coronary arteries to assess heart disease risk. |
| Recommended For | Adults aged 40 and above or with elevated cardiovascular risk but no symptoms. |
| Price | $403.30 NETT and inclusive of GST |
| Appointment Options |
Same-day appointment (subject to availability). Book via WhatsApp: 8893 3757 or email: hello@healthscreening.sg |
| Clinic Locations |
Orchard: 1 Orchard
Blvd #05-09 Camden Medical Centre, S248649 Tanjong Pagar: 72 Anson Rd #01-02 Anson House, S079911 |
What Is a CT Calcium Score Test?
A CT Calcium Score test is a specialised computed
tomography (CT) imaging procedure that measures the amount of hardened
calcium-containing plaque, called calcified plaque, in the coronary arteries.
Calcified plaque indicates the presence of atherosclerosis, a condition that can
progress to coronary artery disease (CAD) and raise the
risk of heart attack or stroke.
The test is primarily used as a screening tool recommended for people aged 40 and above
who may have an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease but have not yet developed
symptoms.


In 2022, nearly 1 in 3 deaths in Singapore was due to cardiovascular disease. Regular screening, including CT calcium score testing, supports early detection of risk and timely preventive measures to protect long-term heart health.
CT Calcium Score Percentile
The test provides a numerical coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, which
reflects the extent of plaque buildup and helps assess the likelihood of
developing CAD.
This score is often compared with results from others in your age and sex group, a
measure known as the percentile. A higher percentile means you have more calcified plaque than your
peers, which may indicate a greater risk of future cardiovascular problems.
| CAC Score | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 0 | No detectable calcium and a very low short-term risk of heart disease. |
| 1 – 99 | Mild plaque is present and there is some increase in cardiovascular risk. |
| 100 – 299 | Moderate plaque burden, associated with increased risk of heart disease. |
| ≥ 300 | Extensive plaque, associated with a high risk of heart attack or other serious cardiovascular events. |
Age also plays a major role in interpreting results, as calcium buildup generally increases over time. A score that is considered high for a younger person may be closer to average for an older person.
- Ages 40 to 49 – Most people in this age group have little or no calcification. A score above 100 is considered high.
- Ages 50 to 59 – Plaque is more common. A score above 100 indicates increased lifetime risk.
- Ages 60 to 69 – Many have some calcification. Higher scores strongly indicate elevated coronary artery disease (CAD) risk.
- Ages 70 and above – Calcification is common. Percentile comparison helps assess relative risk within this group.
CT Calcium Score vs. Other Cardiovascular Tests


A CT calcium score test focuses specifically on detecting calcified plaque in the coronary arteries, while other cardiovascular tests evaluate different aspects of heart and blood vessel health:
| Test | Purpose | How It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Records the heart’s electrical signals | Detects rhythm irregularities, previous heart attacks, and other conduction problems |
| CT Coronary Angiography (CTCA) | Visualised blood flow in the coronary arteries using a CT scan with contrast dye | Identifies blockages and assesses the condition of coronary arteries |
| Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test | Measures thickness of the carotid artery walls using ultrasound | Detects early signs of atherosclerosis and monitors arterial health |
| Stress Test | Monitor heart performance during exercise or medication-induced stress | Detects significant blockages and evaluates cardiovascular fitness |
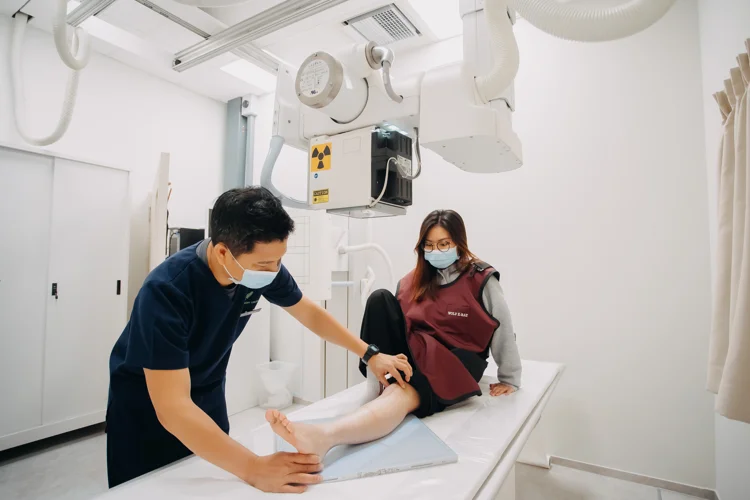
How Is a CT Calcium Score Test Done?
A CT calcium score test is a short, non-invasive procedure designed to capture detailed images of the coronary
arteries.
During the scan, you will lie on a motorised table that slides into the CT scanner. Electrodes
will be attached to your chest to synchronise the imaging with your heartbeat. The scanner takes
rapid, high-resolution images, and you may be asked to briefly hold your breath to reduce
movement and ensure clear results.
After the scan, a radiologist reviews the images to measure the amount of calcium in your
coronary arteries.

Interpreting CT Calcium Score
After your test, your doctor will review both your CT calcium score and its percentile ranking with you. Based on these results, they may recommend preventive measures such as lifestyle changes, medication, or additional testing.

How Much Does a CT Calcium Score Test Cost?
At healthscreening.sg, we provide the CT calcium score test as part of our range of cardiovascular assessments, with the prices as follows:
| Test | Price* |
|---|---|
| Consultation | From $49.05 |
| CT Calcium Score Test | $403.30 |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | $49.05 |
| Treadmill Stress Test with ECG | $218 |
| 2D Echocardiogram | $436 |
| Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test | $163.50 |
| CT Coronary Angiogram | From $1,384.30 |
*Prices are NETT and inclusive of GST.
^Prices last updated on
Jan 28, 2026. While every effort is made to keep pricing information up to date, please contact our team to confirm the latest rates.
How Long Does a CT Calcium Score Test Take?
A CT calcium score test is a relatively quick procedure, usually taking about 30 to 60 minutes from arrival to completion during off-peak hours. For guidance on the best time to schedule your appointment, please contact us.
How to Prepare for a CT Calcium Score Test?
Preparing for a CT calcium score test is simple and involves a few basic steps:
- Avoid caffeine and strenuous activity for several hours before your appointment, as these can affect your heart rate.
- Wear comfortable clothing, but be prepared to change into a medical gown.
- Avoid wearing metal items, such as jewellery, hairpins, and eyeglasses, as you will need to remove them for the scan.
- Inform your doctor about any medications you are taking and any existing medical conditions, especially those affecting the heart.
Our clinic staff will provide you with detailed instructions when you book your appointment.
How to Book an Appointment for a CT Calcium Score Test?
Why Choose Us?







Navigate Easy With Google Maps
Health Screening Singapore (Anson House)
Nearest MRT: EW15 Tanjong PagarHealth Screening Singapore (Camden Medical Centre)
Nearest MRT: TE13 Orchard BoulevardHealth Screening Singapore (CPF Jurong Building)
Nearest MRT: NS1/EW24 Jurong EastFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A normal CT calcium score is 0, meaning no detectable calcium in the coronary arteries and a very low short-term risk of heart disease. Any score above 0 indicates some plaque buildup, with higher scores reflecting greater risk. It is advisable to consult a doctor for interpretation of your test results in the context of your age, sex, and overall health profile.
A CT calcium score test can be valuable for assessing coronary artery disease risk, especially in individuals with borderline or intermediate cardiovascular risk. It provides information on calcified plaque that may not be detected by other tests. Consulting a doctor can help determine if this screening is appropriate for your health profile and risk factors.
A high CT calcium score indicates significant calcified plaque in the coronary arteries, which increases the likelihood of narrowing or blockage. However, it does not measure the degree of blockage directly. Further tests, such as CT angiography, may be required to assess severity. It is advisable to consult a doctor or cardiologist to determine if additional evaluation is needed.
If your calcium score is high, your doctor may recommend lifestyle modifications, medications, and further diagnostic testing to manage your cardiovascular risk. The goal is to prevent plaque progression and reduce the likelihood of heart attack or stroke.
Existing calcified plaque cannot be removed, but its progression can often be slowed or stabilised through healthy lifestyle habits, cholesterol-lowering medication, and controlling blood pressure and other risk factors. Based on your test results, your doctor will advise on a personalised prevention and management strategy tailored to your health profile.
Many people with a high calcium score can live long, healthy lives if their condition is well managed. Treatment typically focuses on controlling cardiovascular risk factors through medication, diet, exercise, and regular monitoring. It is advisable to consult your doctor to develop and follow a long-term plan for maintaining your heart health.
The need for a stent is determined by symptoms and the severity of coronary artery narrowing, not solely by the calcium score. A high score may prompt further imaging, such as CT angiography, to assess blockages. It is best to consult your doctor or cardiologist to interpret your results in the context of your age, sex, and overall health profile to determine whether follow-up testing is needed.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats such as those from fish, nuts, and olive oil can help slow plaque progression. Limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars is recommended, as these can contribute to higher cholesterol levels, inflammation, and further plaque buildup. It is best to consult your doctor, who can provide tailored dietary recommendations based on your test results and overall health profile.
A CT calcium scan is a widely used, non-invasive method for detecting and measuring calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. It reliably identifies the presence of atherosclerosis but cannot detect soft plaque or directly assess the degree of artery narrowing. If you are unsure whether this test is suitable for you, it is best to consult a doctor who can provide guidance based on your health profile.
Generally, a calcium score above 300 indicates extensive plaque and a significantly higher risk of heart attack or other serious heart disease. Scores between 100 and 299 suggest moderate plaque and an increased risk. It is advisable to discuss your results with your doctor, who can interpret them in the context of your age, sex, and overall health profile.
Calcium deposits in arteries cannot be removed, but further buildup can be slowed or prevented. Lifestyle changes, cholesterol-lowering medications, and controlling blood pressure are commonly recommended. It is best to consult your doctor, who can provide personalised guidance on prevention and long-term management.
There is no single “normal” score for all ages, but a score of 0 is considered optimal at any age. Higher scores indicate more calcified plaque and increased cardiovascular risk. Percentile rankings, which compare your score to others of the same age and sex, help put results into context. It is advisable to review your score and percentile with your doctor for personalised interpretation.
An increased calcium score indicates progression of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. This may result from factors such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, or diabetes. It is best to consult your doctor, who can interpret your results and recommend strategies to slow further progression and reduce cardiovascular risk.
